Sexual Reproduction
Sexual Reproduction: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Menstrual Cycle, Fertilization, Puberty, Zygote, Gametogenesis, Endogamy, Oestrus Cycle, Oviparous Animals, Gonadotropins, Viviparous Animals, Syngamy, Embryogenesis, External Fertilisation and, Internal Fertilisation
Important Questions on Sexual Reproduction
In which of the following phases all organisms have to pass through it before they can reproduce sexually?
Which of the following hormones play important role in menstrual cycle?
Read the graph given below and identify the period of follicular phase:
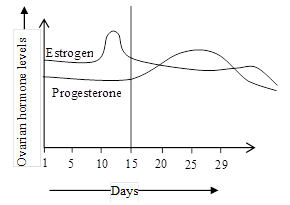
Organisms with relatively simple body organisation commonly reproduce through asexual means but shifts to sexual reproduction:
Why the internal fertiliszation is better than external fertilisation?
Inter flower period is juvenile or mature?
If gametes are produced after reduction division, they are termed as:
Both male and female reproductive structures are present on same plants in –
Exogamy in plants is the term where pollination takes place between flowers of the same plant.
Exogamy is also called as _____.
Differentiate between exogamy and endogamy.
What is the carrier of  gamete in the Pinus, Marchantia, Mango, Chara, and Funaria respectively?
gamete in the Pinus, Marchantia, Mango, Chara, and Funaria respectively?
[where Pollen tube, ]
Synchrony between the maturity of sexes and release of many gametes is shown by:
Select correct option w.r.t. chromosomes number in sexual life cycle of apple.
Clear cut distinction between vegetative, reproductive and senescent phase is shown by
Which of the following plants produce non-motile male gametes?
Male and female sex organs are present on separate plant bodies in all, except
Choose the correct option.
A. Zygotes are universally diploid
B. Zygotes form embryos through mitosis
C. Gametes are universally haploid
D. Gametes are always produced by meiotic cell
